반응형
다항식 회귀 (Polynomial Regression)이란
다항식 회귀 분석은 관계를 n차 다항식으로 추정하는 다중 선형 회귀 분석의 특수한 경우로 알려진 선형 회귀 분석의 한 형태입니다. 다항식 회귀 분석에서는 특이치에 민감하므로 하나 또는 두 개의 특이치가 있는 경우에도 성능에 좋지 않은 영향을 미칠 수 있습니다.
Linear Regression
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 5 * X + np.random.randn(100, 1)
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X, y)
X_vals = np.linspace(0, 1, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
y_vals = reg.predict(X_vals)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.plot(X_vals, y_vals, color="r")
plt.show()
|
cs |

y 값에 0을 곱했을 때 (noise 無)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 5 * X + 0 * np.random.randn(100, 1)
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X, y)
X_vals = np.linspace(0, 1, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
y_vals = reg.predict(X_vals)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.plot(X_vals, y_vals, color="r")
plt.show()
|
cs |

y 값에 5을 곱했을 때 (noise 多)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = np.random.rand(100, 1)
y = 4 + 5 * X + 5 * np.random.randn(100, 1)
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X, y)
X_vals = np.linspace(0, 1, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
y_vals = reg.predict(X_vals)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.plot(X_vals, y_vals, color="r")
plt.show()
|
cs |
Linear Regression with Quadratic Function (2차 함수)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = 4 * np.random.rand(100, 1) - 2
y = 4 + 2 * X + 5 * X**2 + np.random.randn(100, 1)
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X, y)
X_vals = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
y_vals = reg.predict(X_vals)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.plot(X_vals, y_vals, color="r")
plt.show()
|
cs |

다항식 회귀 (Polynomial Regression)
Polynomial Regression with Quadratic Function (noise 少)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = 4 * np.random.rand(100, 1) - 2
y = 4 + 2 * X + 5 * X**2 + np.random.randn(100, 1)
poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2, include_bias=False)
X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(X)
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X, y)
X_vals = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
X_vals_poly = poly_features.transform(X_vals)
y_vals = reg.predict(X_vals_poly)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.plot(X_vals, y_vals, color="r")
plt.show()
|
cs |
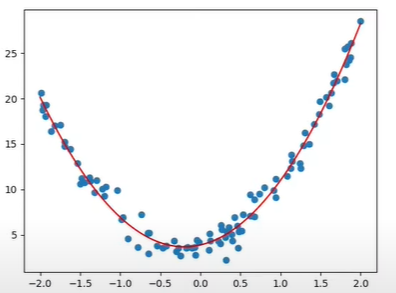
Polynomial Regression with many noise (noise 多)
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
X = 4 * np.random.rand(100, 1) - 2
y = 4 + 2 * X + 5 * X**2 + 10 * np.random.randn(100, 1)
poly_features = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2, include_bias=False)
X_poly = poly_features.fit_transform(X)
reg = LinearRegression()
reg.fit(X, y)
X_vals = np.linspace(-2, 2, 100).reshape(-1, 1)
X_vals_poly = poly_features.transform(X_vals)
y_vals = reg.predict(X_vals_poly)
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.plot(X_vals, y_vals, color="r")
plt.show()
|
cs |
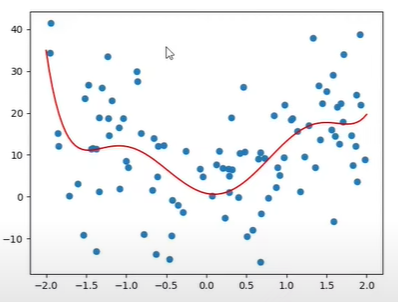
반응형
'공부 > 파이썬 Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python으로 전처리 파이프라인 설계하기 (3) | 2022.03.22 |
|---|---|
| 카운터와 딕셔너리의 차이 in Python (0) | 2022.03.20 |
| 칼로리 트래커 / 대시보드 (1) (0) | 2022.03.18 |
| 비밀번호 관리 매니저 만들기 using Python (0) | 2022.03.18 |
| Pygorithm으로 알고리즘 공부하기 (0) | 2022.03.17 |



댓글