반응형
정렬 알고리즘 시각화하기
1. 파이썬으로 버블 정렬 시각화하기
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
# importing necessary libraries
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
amount = 15
# declaring random variables
# a list that has fifteen random integers between 0 and 100
lst = np.random.randint(0, 100, amount)
# a list that has fourteen integers from 0 to 14
x = np.arange(0, amount, 1)
# bubble sort
n = len(lst)
for i in range(n):
for j in range(0, n-i-1):
plt.bar(x, lst)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.clf()
if lst[j] > lst[j+1]:
lst[j], lst[j+1] = lst[j+1], lst[j]
# visualizing bubble sort
plt.show()
|
cs |
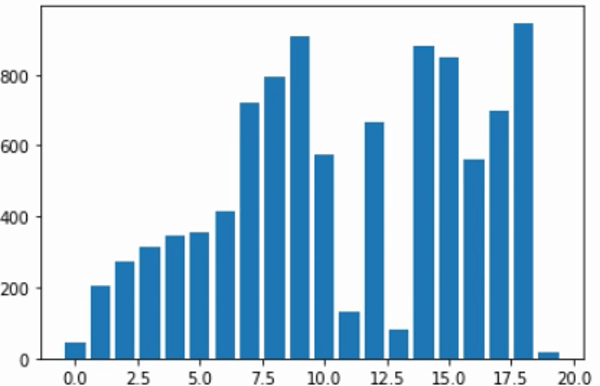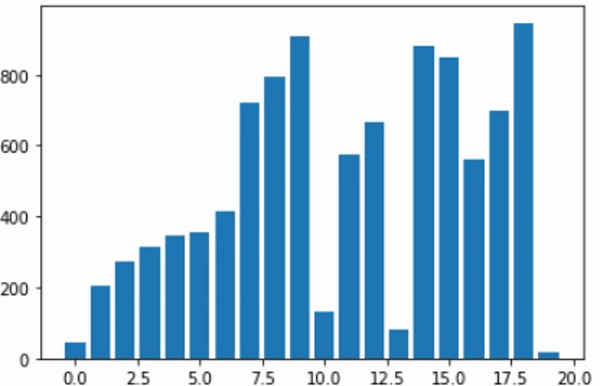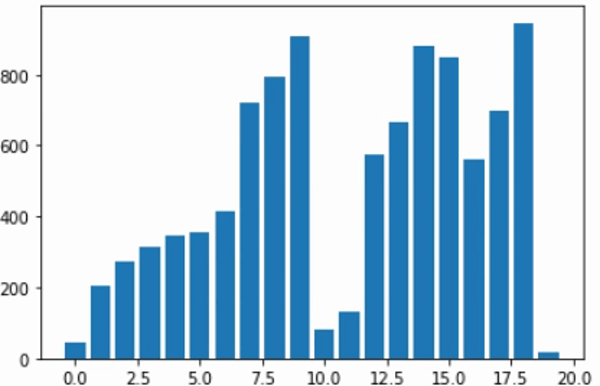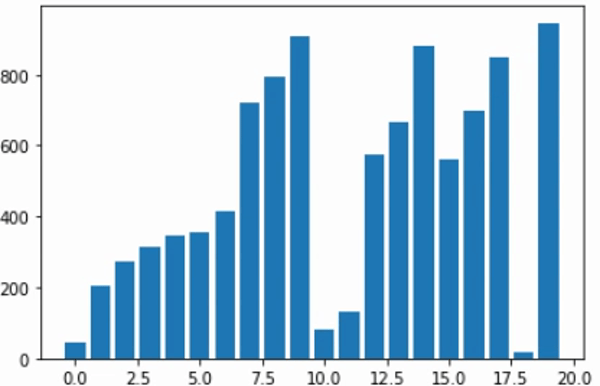
합병 정렬 (Merge Sort) 시각화하기
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
|
import random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
random.seed('ABC')
amount = 20
numbers = [random.randint(0, 1000) for _ in range(amount)]
def merge_sort(number_list, left, right):
# base case
if left >= right:
return
# find the middle
mid = (left + right) // 2
# split recursively into left and right halves
merge_sort(number_list, left, mid)
merge_sort(number_list, mid + 1, right)
plt.bar(list(range(amount)), number_list)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.clf()
#merge the two results
merge(number_list, left, right, mid)
plt.bar(list(range(amount)), number_list)
plt.pause(0.01)
plt.clf()
def merge(number_list, left, right, mid):
# copy left and right halves into new lists
left_cpy = number_list[left:mid + 1]
right_cpy = number_list[mid + 1:right + 1]
# counters indicating the progress
l_counter, r_counter = 0, 0
sorted_counter = left
# until we reach the end of one half
while l_counter < len(left_cpy) and r_counter < len(right_cpy):
# pick the smaller element and put it into the next position
# and progress the counters
if left_cpy[l_counter] <= right_cpy[r_counter]:
number_list[sorted_counter] = left_cpy[l_counter]
l_counter += 1
else:
number_list[sorted_counter] = right_cpy[r_counter]
r_counter += 1
sorted_counter += 1
while l_counter < len(left_cpy):
number_list[sorted_counter] = left_cpy[l_counter]
l_counter += 1
sorted_counter += 1
while r_counter < len(right_cpy):
number_list[sorted_counter] = right_cpy[r_counter]
r_counter += 1
sorted_counter += 1
merge_sort(numbers, 0, len(numbers) - 1)
print(numbers)
plt.bar(list(range(amount)), numbers)
plt.show()
|
cs |
반응형
'공부 > 파이썬 Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Python으로 캔들스틱 주가 시각화하기 (0) | 2021.12.21 |
|---|---|
| Google Colab에서 오디오북 리더 만들기 (feat. Python) (3) | 2021.12.20 |
| TDD - Test-Driven Development(테스트 주도 개발)이란 (0) | 2021.12.11 |
| SW 교육동영상 공모전 소스 (Computer Science, sentdex) (0) | 2021.04.15 |
| 에브리타임 글/댓글 Word 파일로 만들기 (0) | 2021.03.27 |



댓글